Is Covenantal vs Dispensational just a terminology difference?
Upvote:3
Because this is a Protestant controversy, I was not familiar with the terms. However, a bit of light research has led me to understand what the difference is.
Essentially, Dispensationalists hold to a real distinction between Ethnic Jews and Ethnic Gentiles, which still affects relation to God today, whereas Convental theologians hold that the Church is the New Israel:
If we may speak of the two systems in their unqualified forms, dispensationalism asserts that God still has future plans for the Jewish people and deduces that the Church is not spiritual Israel; covenant theology asserts that the Church is spiritual Israel and deduces that God has no future plans for the Jews different than his plans for any other people. (Akin, Jimmy. Israel and the Church)
Dispensationalism began in nineteenth-century England and has undergone various revisions. However, what is unique to all its forms is the Israel-church distinction, dependent on a particular understanding of the covenants. For dispensationalists, Israel refers to an ethnic, national people, and the church is never the transformed eschatological Israel in God’s plan... The church, then, is distinctively new in God’s plan and ontologically different from Israel... Although covenant theology recognizes the plurality of the covenants, it subsumes all post-fall covenants under the overarching category of the covenant of grace. As a result, the Israel-church relationship is viewed in terms of continuity — that is, the two by nature are essentially the same, yet administered differently. For this reason, Israel and the church are constituted as a mixed people (elect and non-elect), and their respective covenant signs (circumcision and baptism) signify the same spiritual reality — hence why baptism may be applied to infants in the church. (Wellum, Stephen. Dispensational or Covenantal? The Promise and Progress of Salvation in Christ)
Given the above, I think the framing of the question is what is contributing to the confusion. It is not the case that Covenentals and Dispensationalists differ on whether to divide parts of the bible, but in how they divide it up. Dispensationalists tend to see ethnic differences between Jews and Gentiles as important even after the life, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ, and Covenentals do not.
Upvote:4
There is a spectrum between the extremes of Covenant Theology and Dispensationalism, but in short they represent two sides of the continuity and discontinuity debate over the Old and New Testaments.
Dispensationalism says there is no substantial continuity between Israel in the Old Testament and the Church in the New Testament. In fact, even within the Old Testament and the New Testament there are multiple dispensations in which God interacts with humanity in very different ways. These dispensations can be unexpected: there are three dispensations in only the first 11 chapters of Genesis, but no dispensation focused on David and the Davidic Covenant. In this diagram from gracegospelpress.org each of the arrows represents a dispensation in which God's primary way of interacting with God's people was different:
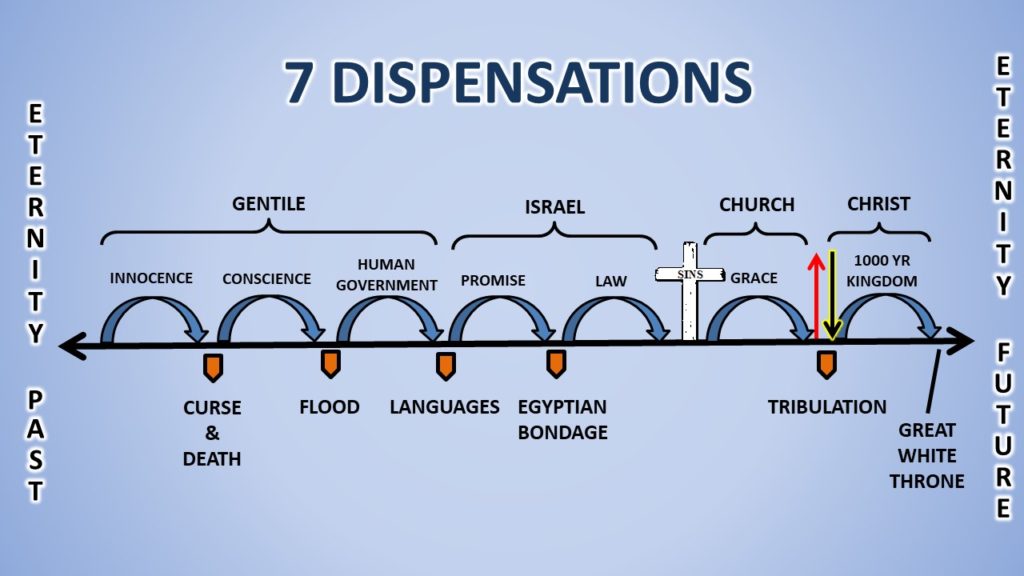
The implications of Dispensationalism are seen most clearly in how they understand the promise/covenant of the Promised Land: the promise that the territory of Israel would belong to Abraham's descendants forever belongs to the people of Israel forever. While this promise was partially fulfilled during the time of the Monarchy, it is still waiting for its final fulfillment. So Dispensationalists usually anticipate that the biological nation of Israel (not necessarily the current country of Israel) will gain control of the entire land promised in Genesis 15, from the "Wadi of Egypt to the Euphrates". This is entirely separate from God's dealings with the Church. Many descendants of Abraham will also be part of the Church, but being part of the Church doesn't mean you'll be part of Israel. This focus on the fulfilment of Abraham's covenant as he would've understood it (and not just spiritualised away into the idea of inheriting the Kingdom of Heaven) leads most Dispensationalists to focus on an earthly eschatology, a pre-millennial return of Christ and a 1000 year reign of Christ in the current Middle East.
Covenant Theology represents the extreme in the other direction, that we should not see any real discontinuity between Old and New. You might expect from the name that Covenant Theology would be focusing on the Biblical covenants of Noah, Abraham, Mosaic, David, and New, but that's not actually the case. Instead Covenant Theology refers to the three "theological" covenants: the Covenant of Works, that God would give life to humanity as long as they remained righteous, the Covenant of Grace, in which God would save his people, and the Covenant of Redemption, which is a covenant between the persons of the Trinity, in which the Father appointed the Son to be the one to become incarnate and die for the atonement of God's people. The Biblical covenants are considered administrations of the singular Covenant of Grace, which means that each of the Biblical covenants has the same purpose, the same covenant parties, and the same benefits, so that the differences between the Biblical covenants are considered to only be incidental. It is because the covenant parties are considered to be one, the People of God, that Israel and the Church are considered to be One people, or why people say that the Church is the New Israel.
Because there is ultimately only one covenant between God and his people, and because there is only one people of God, Covenant Theology does not anticipate a earthly fulfilment of God's promise of the land of the levant. In this era of the church, the promise of the land is seen as being taken up inside the larger promise of the spiritual Kingdom of God; in the future it will be expanded again into the New Heavens and New Earth. But even if there would be in some sense a land of Israel in the New Earth, the promise wouldn't have any particular connection to that land. In the administration of the Abrahamic Covenant the promise of the land of God was seen as referring to the land that Abraham walked, but in subsequent administrations the same promise is now seen as referring to a larger land. In essence, the eternal promise was not to a particular piece of real estate, but instead that God would provide a home for his people. That real estate can change, but the promise to provide it does not.
So no, it's definitely not just a matter of terminology. Dispensationalism doesn't focus on the covenants - only four out of the conventional seven dispensations align with a Biblical covenant, and there is no distinct dispensation for one very important Biblical covenant, the Davidic Covenant. And on the other hand, Covenant Theology does not actually refer to the Biblical covenants, but the "theological" covenants of Works, Grace, and Redemption.
To return to the beginning, Covenant Theology and Dispensationalism represent the extremes of continuity and discontinuity, but they are not the only frameworks Protestants have for understanding how the Old and New Testaments work together. In particular, Reformed Baptists in the US have been doing a lot of good work in recent decades to find some middle paths between continuity and discontinuity. In my opinion their frameworks give a more appropriate emphasis to the Biblical covenants than either Covenant Theology or Dispensationalism do, and I think it's likely their popularity will grow globally in the future. Look out for names like Beale, Gentry, Wellum, and Zaspel.
More post
- 📝 Why have a photo of the bishop in the sacristy?
- 📝 Aren't Romans Catholics cults? As they have different doctrine comparing to Christianity
- 📝 Need help understanding something from the dubia around Traditionis Custodes
- 📝 May Christians work while fasting?
- 📝 How do believers in the tripartite nature of man (body, soul and spirit) explain Jesus' omission of the word "spirit" in Matthew 10:28?
- 📝 Why does Calvinism need the doctrine of Perseverance of the Saints if it believes in Unconditional Election?
- 📝 According to Protestant interpretations of the Bible, is there justification for “disliking somebody”?
- 📝 What is the earliest historical instance of state-paid Clergy?
- 📝 At what date in history was the last papal anathema officially applied through the death penalty in a papal court against a heretic or protestant?
- 📝 Has the matter of salvation - whether it is by works or by faith alone - ever been considered on any councils of the Catholic and Orthodox churches?
- 📝 What is the story behind a monk’s tonsure?
- 📝 How are angels and humans different?
- 📝 What writing materials did the writers of the Gospels use?
- 📝 What is the basis of my fractured understanding of "Sola Scriptura"?
- 📝 Why are the men of Genesis so old? Were the dating systems just different? Are all of these old ages supposed to have symbolic meaning?
- 📝 Are there any spiritual benefits in writing a diary?
- 📝 When did the demon announce they were afraid of God?
- 📝 Do Protestants believe Jesus and Satan are brothers?
- 📝 In what form did water exist before the creation of light?
- 📝 What is theological root of global warming skepticism?
- 📝 Which Christian groups or denominations believe in modern-day Theophanies?
- 📝 Why did Paul say "I am pure from the blood of all men"?
- 📝 Does the RCC allow confirmation names that aren't based on saints?
- 📝 Are Christians allowed to practice Eastern martial arts?
- 📝 What do Latter Day Saints believe happens to persons who have rejected Christ Jesus?
- 📝 Have Christians opposed "Good Luck" wishes?
- 📝 What is the basis of the Jehovah's Witnesses' belief that Jesus died on a Stake instead of a Cross?
- 📝 Is Satan's kingdom here on earth?
- 📝 How to interpret the ban of unions between believers and non-believers?
- 📝 Why don't Presbyterians have altars?
Source: stackoverflow.com
Search Posts
Related post
- 📝 Is Covenantal vs Dispensational just a terminology difference?
- 📝 What is the difference between Evangelical and Protestant?
- 📝 Why can't Catholicism just drop its Marian devotion?
- 📝 How can I tell the difference between the Moral law and other laws in the old testament?
- 📝 What were the Nephilim, and what role did they play in the Bible beyond just being mentioned?
- 📝 What is the difference between Reformed and Presbyterian
- 📝 Why the difference in depiction of the cross between Catholics and Protestants?
- 📝 What is the difference between 'Biblical' and 'Systematic' theology?
- 📝 What is the Difference Between ROCOR-MP and ROCOR-A (ROCA)
- 📝 Difference between Augustinianism and Calvinism
- 📝 What was the difference between the Pharisees and Sadducees?
- 📝 What is the difference between icons and idols in churches that permit icons?
- 📝 What is the difference between the doctrines of "Perseverance of the Saints" and "Eternal Security?"
- 📝 What is the difference between "infallible" and "inerrant"?
- 📝 What is the difference between "catholicism" and "catholic"?
- 📝 What is the difference between a pastor, a priest, and a minister?
- 📝 What is the difference between justification and sanctification?
- 📝 Is God just and/or merciful?
- 📝 Is there a significant difference between salvation by faith with works and salvation by faith and works?
- 📝 What is the difference between a Bible College and a Seminary?
- 📝 Why is rejection of the Trinity heresy, and not just wrong? (Protestant perspective)
- 📝 Was there doctrinal difference between Lollards and Waldenses?
- 📝 What is the difference between classical and revised dispensationalism?
- 📝 What's the difference between judging God and questioning God?
- 📝 What is the difference between man's soul and spirit?
- 📝 What is the difference between "Catechism" and "Canon Law" in Catholicism?
- 📝 How to get the most out of the Bible with just one reading?
- 📝 Is there a difference between Liberal, Progressive, and Emergent Christianity?
- 📝 Is this distinction of biblical "love" terminology compatible with scripture?
- 📝 What is the difference between a covenant and a contract?
