Interesting Facts, History & Information About San Antonio Missions

- By
- Aparna Patel
- |
- 11 Mar, 2023
- |
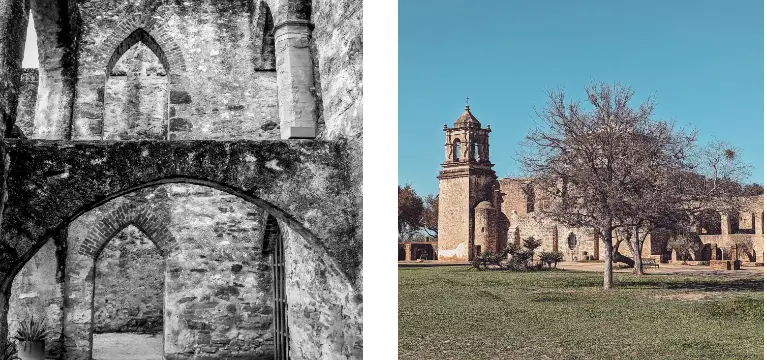
San Antonio Missions are a series of five Spanish colonial missions located in San Antonio, Texas. These missions were built in the 18th century by Spanish Franciscan friars as part of their efforts to convert indigenous peoples to Christianity and expand the Spanish Empire in North America.
Today, the San Antonio Missions are recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a significant cultural and historical treasure. In this blog, we will explore the interesting facts, history, and information about the San Antonio Missions, including their architecture, religious and cultural significance, and their role in shaping the history of Texas and the United States.
Interesting facts about San Antonio Missions
- San Antonio Missions National Historical Park is located in San Antonio, Texas and comprises four Spanish colonial missions: Mission Concepción, Mission San José, Mission San Juan, and Mission Espada.
- The park was established in 1978 and was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 2015.
- The missions were established in the 18th century by Spanish friars to spread Christianity among the local indigenous people and to extend Spanish influence in the region.
- The park includes not only the missions themselves but also surrounding farmland, historic acequias (irrigation systems), and the San Antonio River.
- San Antonio Missions National Historical Park is one of the most-visited national parks in Texas, with over 1.5 million visitors each year.
- The architecture of the missions is a blend of Spanish, European, and indigenous styles, with some of the buildings featuring intricate carvings and brightly-colored frescoes.
- The missions were also centers of agriculture and industry, with the friars teaching the indigenous people to farm and raise livestock, and to make goods such as textiles and pottery.
- Today, the missions continue to serve as active Catholic parishes, and their surrounding communities are home to a diverse mix of cultures and traditions, reflecting the region’s rich history.
Information & History of San Antonio Missions
The San Antonio Missions are a group of four Spanish colonial missions located in San Antonio, Texas. They were established in the 18th century by Catholic missionaries to spread Christianity among the Native Americans in the area. The missions were also used as centers of agriculture and trade, and played a significant role in the development of the region.
The four missions included in the San Antonio Missions National Historical Park are:
- Mission San Antonio de Valero (the Alamo)
- Mission Concepción
- Mission San José
- Mission San Juan Capistrano
All four missions were built between 1718 and 1731, and are known for their unique blend of Spanish and indigenous architecture. They were declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2015, recognizing their importance as a cultural and historical landmark.
Throughout their history, the missions faced numerous challenges, including attacks by Native American tribes, droughts, and political turmoil. They were eventually secularized by the Spanish government in the 1820s, and many of their original structures fell into disrepair.
In the early 20th century, efforts were made to preserve and restore the missions, and they were eventually designated a national historical park in 1983. Today, visitors can explore the missions and learn about their fascinating history and cultural significance.
Read More:
- Monumental Earthworks of Poverty Point: Facts, History & Information
- Monticello and the University of Virginia in Charlottesville : Facts, History & Information
- Interesting Facts, History & Information About Mesa Verde National Park
- La Fortaleza and San Juan National Historic Site in Puerto Rico
- Interesting Facts, History & Information About Independence Hall
- History & Information About The Chaco Culture
FAQ about San Antonio Missions
What are the San Antonio Missions?
The San Antonio Missions are a group of five Spanish colonial missions located in San Antonio, Texas. They were established in the 18th century to spread Christianity among the Native American population and to solidify Spain’s presence in the region.
What are the names of the five San Antonio Missions?
The five missions are: Mission Concepción, Mission San Jose, Mission San Juan, Mission Espada, and the Alamo.
When were the San Antonio Missions established?
The first mission, Mission San Antonio de Valero (the Alamo), was established in 1718. The other four missions were established over the next several decades.
Who built the San Antonio Missions?
The San Antonio Missions were built by Spanish Franciscan missionaries, with the help of Native American laborers and artisans.
What is the significance of the San Antonio Missions?
The San Antonio Missions are a UNESCO World Heritage Site and are considered one of the most important examples of Spanish colonial architecture and design in the United States. They also provide insight into the complex relationships between Spanish colonizers, Native Americans, and the natural environment.
Can I visit the San Antonio Missions today?
Yes, all five San Antonio Missions are open to visitors. They are managed by the National Park Service and offer guided tours, exhibits, and educational programs.
Is there an admission fee to visit the San Antonio Missions?
No, admission to the San Antonio Missions is free. However, some tours and activities may have a fee.
What is the best time of year to visit the San Antonio Missions?
The San Antonio Missions are open year-round, but the best time to visit is in the spring or fall when the weather is mild and there are fewer crowds.
Search Posts
Latest posts
-
5 Mar, 2024
Passing through airport security with autism
-
4 Mar, 2024
How can I do a "broad" search for flights?
-
4 Mar, 2024
Why would you wrap your luggage in plastic?
Popular posts
-
5 Mar, 2024
Why prohibit engine braking?
-
5 Mar, 2024
How to avoid drinking vodka?